Deploy a database that automatically initializes the Schema
We use the container method to deploy database components, especially when the enterprise has a large number of project development business and deploys many development and testing database components.The following problems are often encountered:
- The business needs to use the database, but after the database is deployed, the operation of creating the schema or the creation of some initialization data needs to be performed in the database.
- To develop and test multiple deployment environments, step 1 needs to be repeated many times.
- There are many projects, and the database schema required by the project is not clear after a long time.
- The database schema management is chaotic when the project is delivered.
Now if it is a business system developed in languages such as Go, it has the ability of the ORM layer to automatically initialize and update the Schema. If so, this article is useless to you.But most other development language businesses currently don't have this capability.
If we also manage the database as a service module in a business, we hope that the initialization of the schema can be completed directly after the service is started, and the data service capability can be provided directly.
So how to achieve such an effect in Rainbond?
Schema initialization generally has two schemes in the traditional:
- Manual import after database startup; manual operation through the client, no automation at all;
- Connect to the database for initialization when the business service starts, depending on the capabilities of the business server.
It can be seen that these two methods have their own drawbacks, so is there a way to automatically initialize the specified data when the database is started?The answer is yes!
Let's take MySQL as an example. The official has good support for Docker. First, let's look at a description of Mysql official image on Dockerhub:

When the database container first starts, a new database with the specified name is created and initialized using the provided environment variables. Additionally, it will execute files with extensions 2.sh ,<code>and `found in/docker-entrypoint- </code>. The files will be executed in alphabetical order. By default, SQL files will be imported into the database specified by theMYSQL_DATABASE` variable.Therefore, we only need to maintain the SQL required for database initialization on the basis of the Mysql mirroring working mechanism.We mentioned above that the database is also used as an independent service module. We can also manage Sql and other steps through code and divide version branches.
Rainbond supports a variety of component creation methods. Here we use the method of creating components from source code, write a Dockerfile and upload it to a client that supports the Git/Svn protocol, and then build directly on the platform; this method is transparent and reproducible use and automate builds.
Directory Structure
./
└── Dockerfile
└── config
├── my.cnf
├── conf.d
├── docker.cnf
└── sql
├── init_database
└── README.md
Dockerfile
#Base image
FROM mysql:latest
MAINTAINER Aaron <Aaron_ops@163.com>
#Copy the sql file to the /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/ directory so that this sql can be executed automatically at startup
COPY ./sql/*.sql /docker- entrypoint-initdb.d
#Copy mysql configuration file
COPY ./config/ /etc/mysql/
#Mysql password
ENV MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD rainbond
#Data persistence directory
VOLUME [ "/var/lib/mysql" ]
# Port
EXPOSE 3306
Project address:https://github.com/Aaron-23/Initialize-db
Using this project to build on the platform, Rainbond will automatically detect the environment variables, storage, ports and other information defined in the Dockerfile, automatically configure these configuration items, and automatically start the database after the Dockerfile is built.
It should be noted that MySQL is a stateful service, so you need to change the component type to stateful single instance before building.
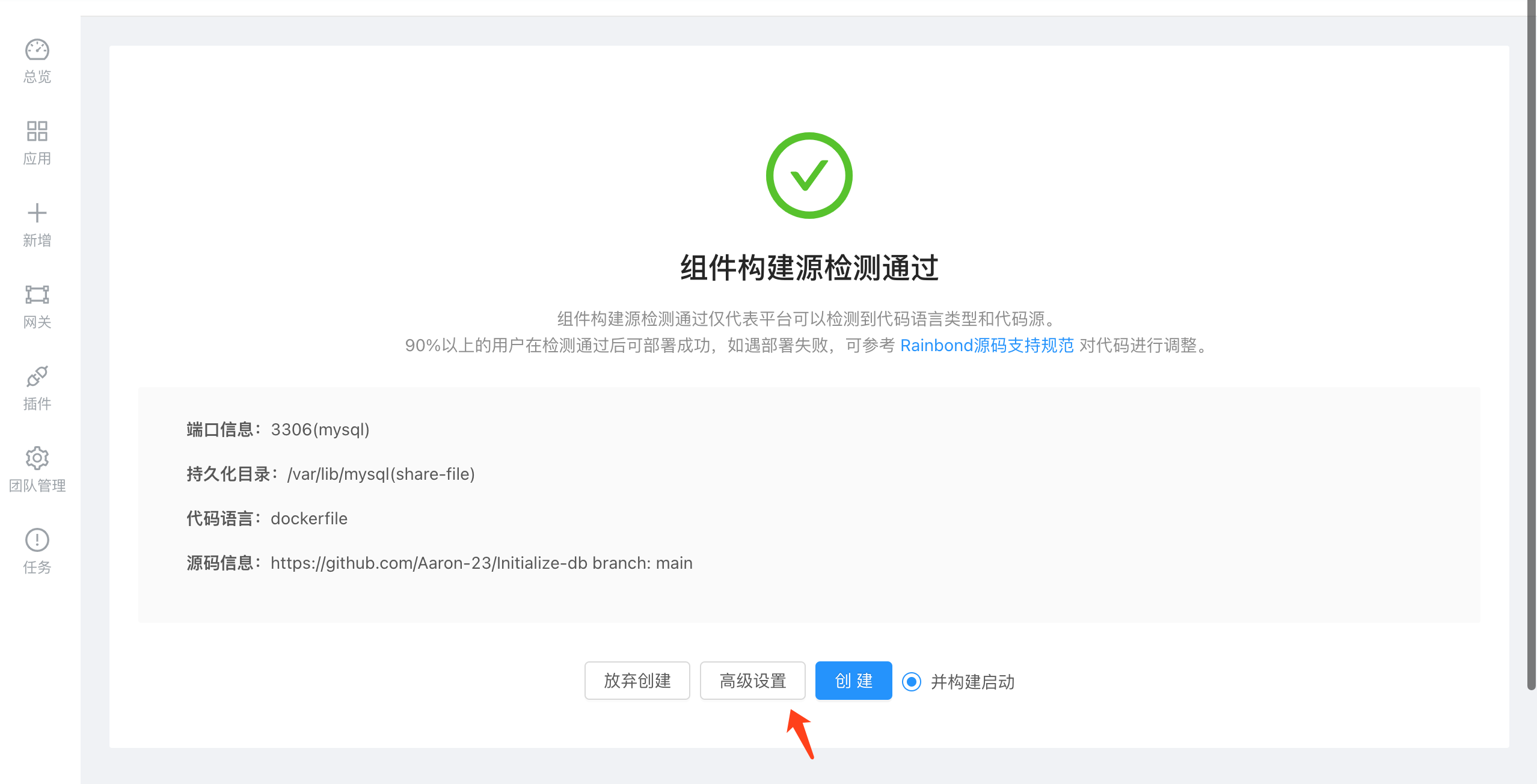

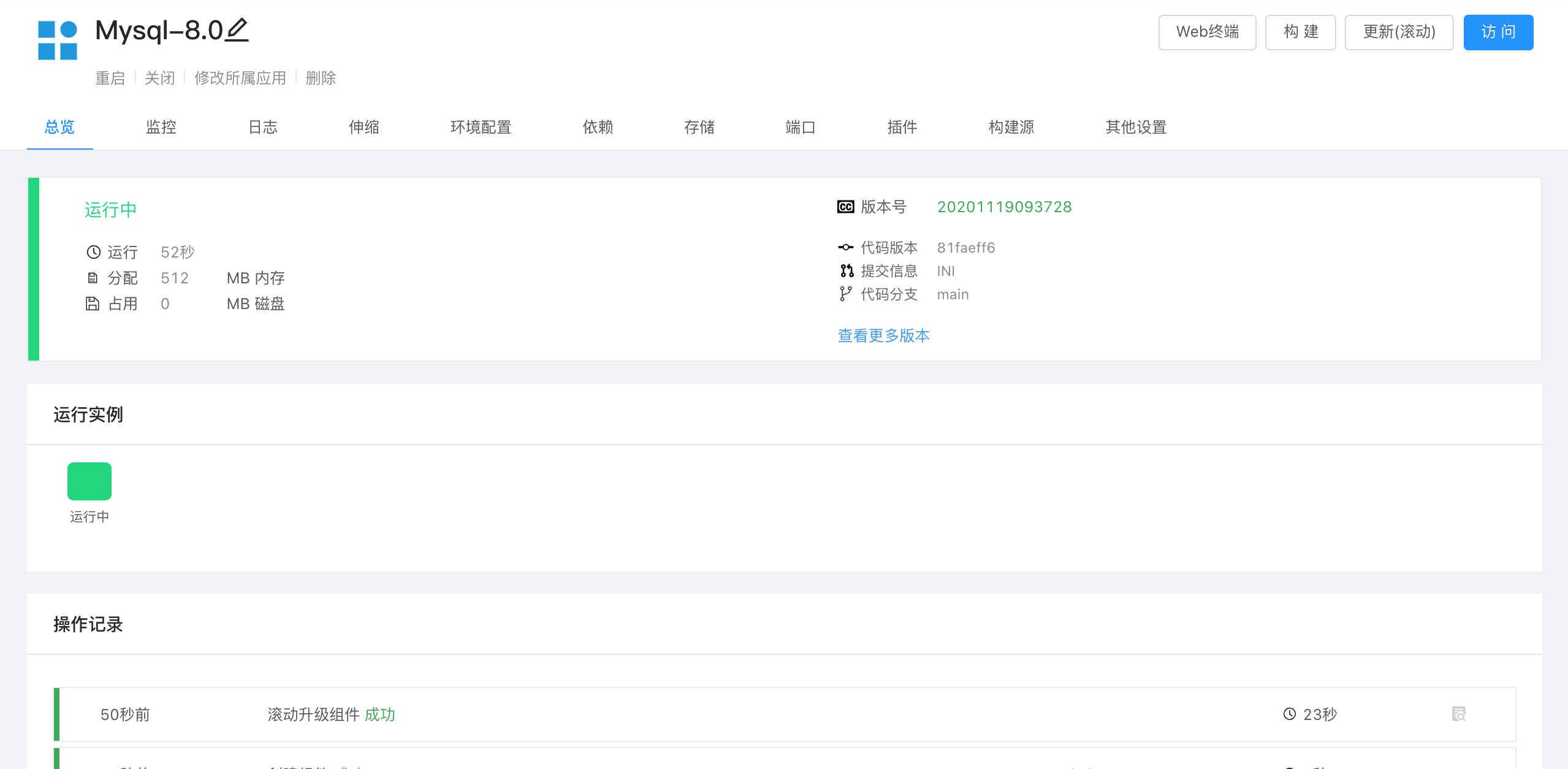
Startup completed, enter the running state
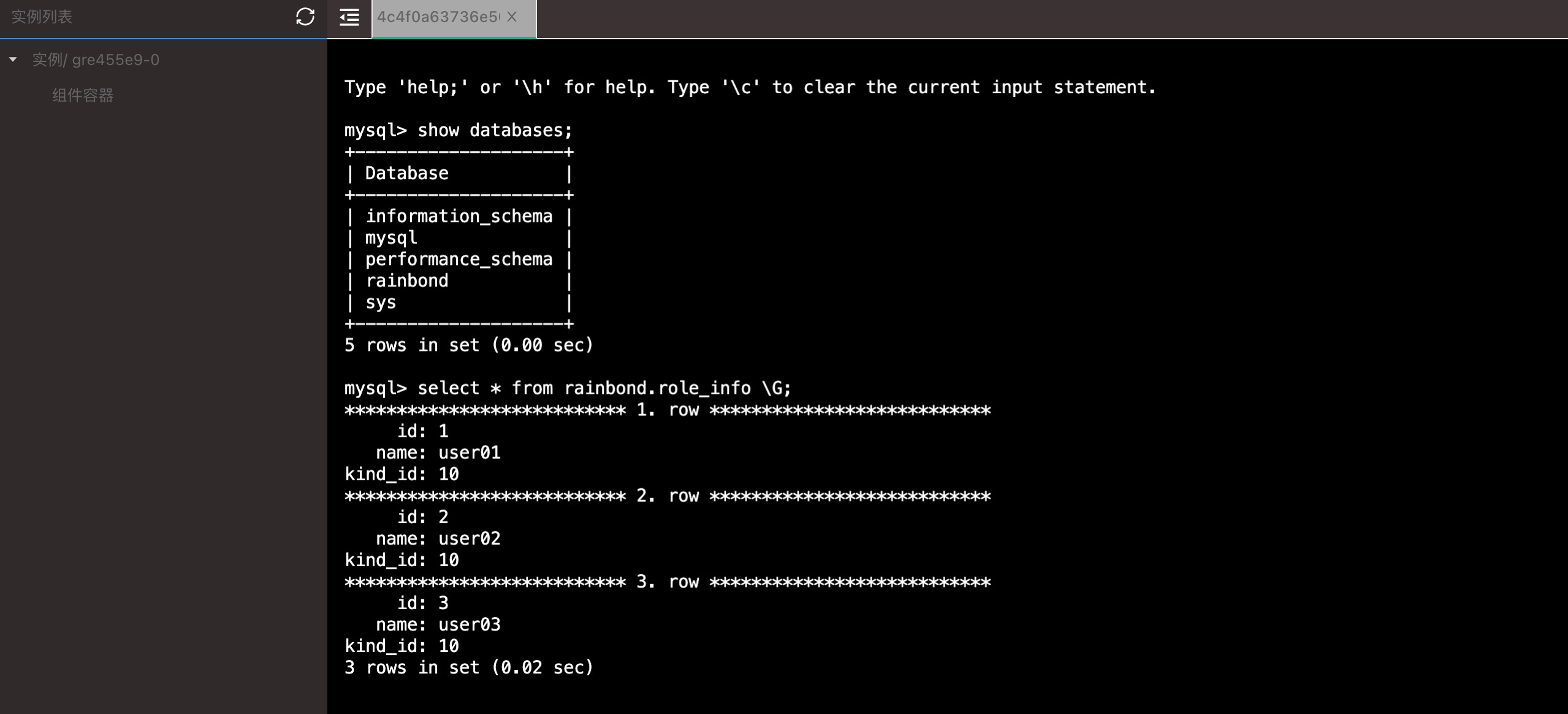
Enter the database through the web terminal to check the relevant data has been initialized
Database initialization in this way does not require modification of program code or external tools. The database can be quickly deployed and initialized through the capabilities of the platform. In the subsequent use process, service operation can be completed through functions such as performance analysis, resource monitoring, and instance scaling. Time-to-time full life cycle management, improve development efficiency and enhance business stability.
In addition, we can also publish this component to Rainbond's internal component library, and the subsequent development, testing and delivery process can directly install this component with one click to obtain database services with initial data completion.
The above MySQL database is only a reference example. Databases such as MongoDB and PostgreSQL all support the same type of data initialization.